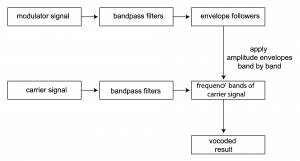
Vocoders were introduced in Section 7.1.8. The implementation of a vocoder is sketched in Algorithm 7.6 and diagrammed in Figure 7.49. The MATLAB and C++ exercises associated with this section encourage you to try your hand at the implementation.
[equation class=”algorithm” caption=”Algorithm 7.6 Sketch of an implementation of a vocoder”]
algorithm vocoder
/*
Input:
c, an array of audio samples constituting the carrier signal
m, n array of audio samples constituting the modulator signal
Output:
v, the carrier wave modulated with the modulator wave */
{
Initialize v with 0s
Divide the carrier into octave-separated frequency bands with bandpass filters
Divide the modulator into the same octave-separated frequency bands with bandpass filters for each band
use the modulator as an amplitude envelope for the carrier
}
[/equation]
[wpfilebase tag=file id=169 tpl=supplement /]
[wpfilebase tag=file id=103 tpl=supplement /]
[wpfilebase tag=file id=71 tpl=supplement /]
[wpfilebase tag=file id=101 tpl=supplement /]
Another interesting programming exercise is implementation of a pitch glide. A Risset pitch glide is an audio illusion that sounds like a constantly rising pitch. It is the aural equivalent of the visual image of a stripe on a barber pole that seems to be rising constantly. Implementing the pitch glide is suggested as an exercise for this section.
1 comment
Comments are closed.